COOPERATION
What are the 4 C's and how do they determine the quality of a diamond?
01
Carat or carat
What does the carat of a diamond mean?
02
Colour of colour
What is the color grading for colorless diamonds?
03
Clarity of purity
What determines the clarity of a diamond?
04
Cut or grinding quality
How important is the cut quality of a diamond?
01
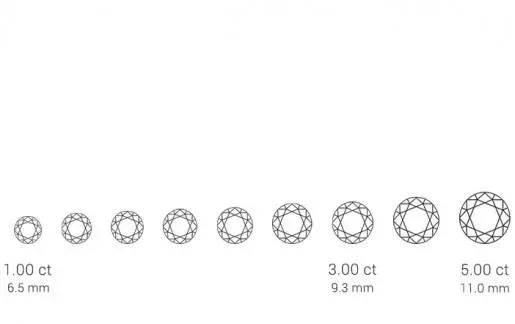
What does the carat of a diamond mean?The carat weight of a loose diamond always indicates the weight of the gemstone. One carat is equal to 200 milligrams. The weight of a gemstone is often expressed with two decimal places or in points on a scale of 100 points. For example, 0.75 carats corresponds to 75 points ct. or 150 milligrams.A higher carat for gemstones of the same type simply means that you are purchasing a larger diamond. When comparing different gemstones, density is important. For example, a diamond has a density of approximately 3.5 g/m3, while amber measures approximately 1 g/m3. So, a 1-carat diamond will be smaller than a 1-carat piece of amber, but they both weigh 200 grams.Although 'carat' in diamonds refers to the weight of the gemstone, the term has a different meaning in gold. There, carat refers to the amount of pure gold in the alloy. For example, 24 carat gold consists of 99.99% pure gold.How are jewelry with multiple gemstones or precious metals valued?The carat weight of a piece of jewelry indicates how much the individual gemstones or diamonds in your jewelry weigh and what their value is. For example, a diamond necklace with 10 stones of 0.30 carat each will weigh a total of 3 carats. In addition to the value of the 4 C's, the precious metal in the jewelry also has an additional value.A carat of diamond is not the same as a carat of gold. In gold, carat refers to the amount of gold that is incorporated into the jewelry. For example, 24 carat gold consists entirely of gold. To ensure good quality and strength of the precious metal, gold jewelry usually consists of 18 carats, which is equal to 75% real gold and 25% other precious metal to strengthen the gold.

02
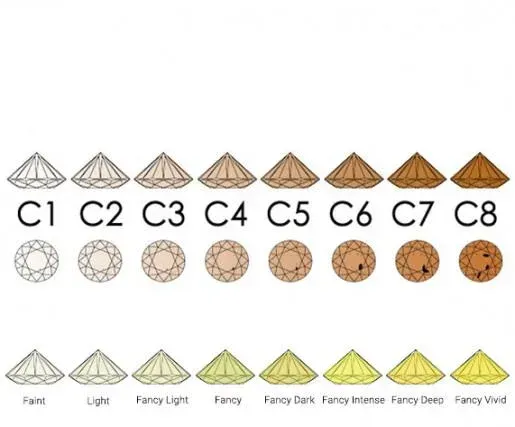
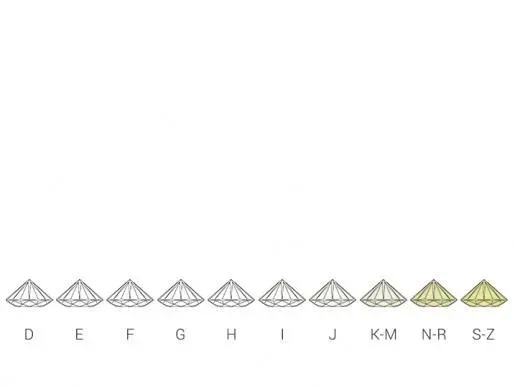
What is the color grade for colorless diamonds? To assess their quality and value, all diamonds are assigned a color grade. Even colorless diamonds are graded on a scale from completely colorless to slight yellow tints. The Gemological Institute of America (GIA) has established an international color set based on letters. The highest valued, purest, and rarest diamonds are colorless and are labeled D, E, or F. If you are planning to invest in a loose diamond, it is recommended that you choose a diamond with a high degree of colorlessness and clarity. Diamonds graded between colorless and Z often exhibit slight tints that are usually only visible under a microscope. Diamonds with the lowest grades and slight yellow tints are labeled S to Z. It is important to note that a slight yellow tint does not mean that the diamond is actually yellow. A diamond must be completely yellow to be considered a fancy colored diamond, which means that it is a diamond that has been chemically changed to a different color. In the past, names such as Jager (D), Wesselton (H) or Lop Cape (N) were used to indicate international colour grades, but these have been replaced by letters to allow for a uniform and international comparison of the quality of diamonds.How are coloured diamonds graded?In addition to colourless and slightly tinted diamonds, there are also coloured diamonds, such as brown, orange, pink, blue, red and green diamonds. Diamonds that retain their colour through a chemical reaction are called "Fancy Coloured", as stated on the diamond certificate.Coloured diamonds are extremely rare, only 1 in 10,000 diamonds shows a natural colour. The most common colours are brown and yellow, while green, red and blue are extremely rare.Coloured diamonds are also graded based on the 4 C's. The colour grade varies from "Faint" for the least coloured diamonds to "Fancy Deep" for diamonds with an intense and deep colour saturation. There are nine grades based on color, saturation, and the type of gemstone. Diamonds with vibrant colors are not only rare, but also very valuable, making them excellent investment opportunities. In addition to diamonds, you can also invest in natural colored gemstones such as emerald, ruby, or sapphire. It is important to remember that a red diamond is not the same as a red ruby, as they are two different gemstones with their own characteristics, qualities, and pricing based on the 4 C's.
03
What affects the clarity of a diamond? The third property of the 4 C's that is determined during the mining of diamonds is clarity. An expert looks at the gemstone through a loupe to magnify the interior of the stone 10 times. Most diamonds have some impurities that affect the clarity of the diamond. These impurities reduce the diamond's ability to reflect light, which is why a diamond with impurities sparkles less than a pure gemstone. A diamond without impurities is considered pure or 'loupe clean' and therefore represents the highest quality. External impurities, caused by damage or wear, are called blemishes. Impurities inside the diamond are formed during the gemstone's formation process and are called inclusions. There are three types of inclusions:Black or dark spots (spots) - dark spots that form during the carbon phaseVeils (clouds) - microscopic, cloud-like inclusions that reduce clarityFragments (plumes or feathers) - molecular breaks in the carbon structure of the diamond. This is the most common type of inclusion.Why are VS diamonds best suited for use in jewelry?It is best to invest in diamonds with good 4C qualities, such as high clarity, to facilitate possible resale later. Diamonds with extremely high clarity, ranging from FL to VVS2, are of course expensive and require a buyer who is willing to pay the same price or more later. However, if you are looking for a more affordable investment, diamonds with VS1 or VS2 clarity are perfectly suited for use in jewelry, such as diamond engagement rings. The price of these diamonds is lower because they are "eye-clean", which means that they contain small impurities that are not or barely visible to the naked eye. Your diamond jewelry therefore looks pure, still retains good quality and is considerably less expensive, but still retains its value as an investment.

04
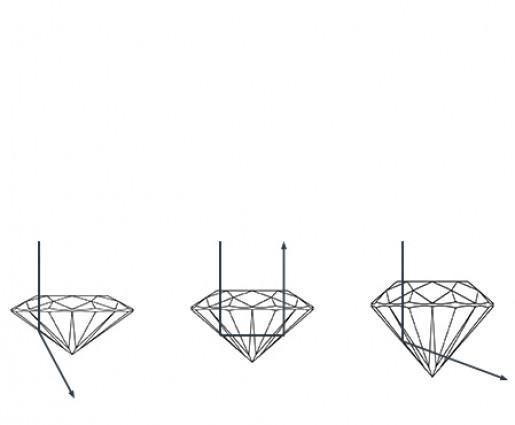
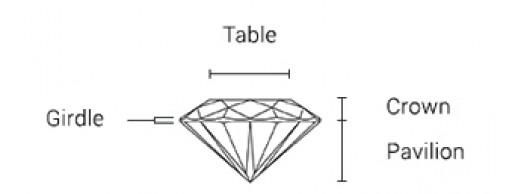
What is the role of the cut quality in a diamond? The cut is the most crucial factor of the 4 C's that determines the quality of a diamond for both jewelry and investment purposes. It is also the only human intervention that can affect its value. Cutting a rough diamond into different facets gives the gem its unique brilliance. The more facets that are created during the cutting process, the better the diamond can reflect light and the more it will shine. How is the specific cut of a diamond achieved? The cut refers to the proportions of the different parts of the cut diamond, the symmetry and the degree of brilliance. The pavilion of a diamond should not be cut too deep or too shallow, as this affects the quality of the light reflection. A poorly cut diamond can lead to light loss or dark areas in the stone. In a well-cut diamond, almost all of the light will shine out through the crown, the top part. The size of the table, the flat surface at the top, varies depending on the cut. The cut of the table can make the diamond appear larger. The girdle, the edge on the side of the diamond, contributes to the strength of the gemstone and can vary from extremely thin to extremely thick. At the bottom of the diamond is a facet called the culet. Since a diamond does not have a point but a tiny flat bottom, a perfectly cut culet contributes to the brilliance of the diamond and prevents light from escaping from the bottom.




